A number of variables have come together to cause Germany’s economic crisis, which is unprecedented. These reasons include de-industrialization and the energy crisis. Below is a summary of this crisis’s underlying causes and consequences:
Energy Crisis:
Germany’s decades-long economic domination was largely due to its reliance on inexpensive Russian gas. However, this energy supply is no longer as dependable or economical as it once was because of the Middle East’s geopolitical unrest and unpredictability. Germany’s businesses are becoming less competitive in the worldwide market as a result of having to import costly energy sources like LNG (Liquid Natural Gas) from the US, Qatar, and Norway.
Effect on Manufacturing: Germany’s high energy costs are reducing profit margins and lowering the competitiveness of German exports. Germany’s manufacturing strength is being undermined by cheaper products made in China and the United States.
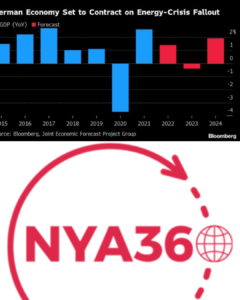
Recession Warning: It is predicted that Germany’s GDP would fall by 0.3% in 2023 as a result of these difficulties. The government has projected 1.3% increase for the upcoming year but given the unpredictability of events like Middle East tensions, this growth estimate is met with skepticism.
Problems with the Supply Chain and Inflation: Rising energy prices and supply chain interruptions are causing high inflation in Germany. The triple danger of rising energy costs, manufacturing declines, and inflation has a significant impact on the economy.
Lack of Innovation: Germany has fallen behind other countries in the auto industry when it comes to electric cars (EVs), which are the industry’s future. In the EV market, Chinese brands are the leaders, followed by US behemoths like Tesla. Volkswagen is a German carmaker that is far behind.
Cost-Based Competition: Price is a key factor in the current global economy. Despite its long history of producing high-quality goods, Germany no longer enjoys the pricing advantage it once did due to its high energy costs and cost structure. For example, the cost of manufacturing Chinese-made EVs can be up to 40% less than that of German-made models.
Outsourcing Labor: Businesses in Germany are being pushed to think about moving to nations like China or the United States that offer less expensive labor and better manufacturing capabilities, due to the country’s labor scarcity and high pay expenses. But this change can also bring with it fresh difficulties and global conflicts.
Demographic Problem: Germany’s labor shortage problem is made worse by the country’s aging population. The UN projects a significant fall in the working-age population, which will affect its industrial base.
Environmental Concerns: Germany’s reliance on coal, especially the harmful lignite coal, to make up for its energy deficit is unsustainable and goes against the country’s objectives for the green energy transition.
Middle East Uncertainty: Germany’s energy situation and expenses are further strained by the continuous unrest in the Middle East, which includes recent events in Israel and the interruption of gas supplies to Egypt.
Germany’s economic future is uncertain, and it can take some time for the country to adjust to these complex problems. It is unclear if Germany will be able to effectively manage this problem and maintain its position as a major economic force in the world because it will be up against fierce competition from nations with more inventive and affordable manufacturing solutions.
Follow us on social media: Instagram, Threads & Twitter @nya360_ YouTube & Facebook @nya360.





